High-efficacy adjuvanted subunit vaccine against variant infectious bursal disease virus in chicks
FAYETTEVILLE, GA, UNITED STATES, July 25, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- A recent study demonstrates that the IBDV VP2 subunit vaccine prepared in this study was able to induce the production of specific antibodies, inhibit bursal atrophy and resist viral attack. The vaccine offers a safer alternative to traditional live-attenuated vaccines, with potential applications in global poultry disease control.
Infectious bursal disease (IBD) is an acute, highly contagious disease caused by the infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV), primarily affecting chicks. Notably, the emergence of new mutant strains that exacerbate the disease can cause serious economic losses to the global poultry industry. To date, there is no commercial vaccine against the new mutant strains.
Paving the way towards that goal, a team of researchers from China developed a novel adjuvanted subunit vaccine-IBDV VP2 subunit vaccine able to induce the production of specific antibodies, inhibit bursal atrophy and resist viral attack.
“IBDV is widely prevalent and is suspected to be related to genetic changes in the VP2 gene, causing immune escape,” explains the study’s senior author, Zongyan Chen, a professor at Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences. “In this study, we used IBDV variant strain isolated in the laboratory to prepare an IBDV subunit vaccine to protect sensitive chicks from IBDV infection.”
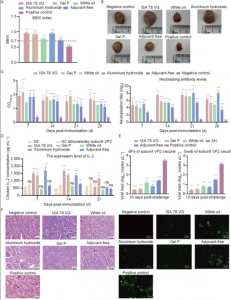
The researchers compared the safety and efficacy of subunit vaccines against the novel variant strain of IBDV VP2 prepared with white oil adjuvant, Montanide™ ISA 78 VG, Montanide™ Gel P and aluminum hydroxide adjuvants, together with a control. Their protective effects were evaluated by tissue dissection, observation of pathological sections, detection of antibody levels, and detection of tissue viral load.
“Under the same dose of antigen (IBDV), the protective effects of ISA 78 VG, Gel P, and aluminum hydroxide adjuvants evaluated were enhanced to prevent infection with this pathogen,” says Chen.
The team’s findings, published in KeAi’s Journal of Integrative Agriculture, provide experimental references and theoretical basis for the subsequent control of IBDV.
References
DOI
10.1016/j.jia.2024.12.007
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jia.2024.12.007
Funding Information
National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1801000) and Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai, China (24ZR1479200).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.